User:Zjdtmkhzt/PathologyGarbage: Difference between revisions
| Line 215: | Line 215: | ||
So let's say we split the following Pathogen:<br/> | So let's say we split the following Pathogen:<br/> | ||
[[Image: SplitPatho1.PNG]]<br/> | [[Image: SplitPatho1.PNG]]<br/> | ||
We will receive the following Segments:<br/> | We will receive the following Segments:<br/> (Plus a 'a62' that I accidentally used up before making the screenshot. :)) | ||
[[Image: SplitPatho2.PNG]] | [[Image: SplitPatho2.PNG]] | ||
Revision as of 14:04, 23 November 2020
A pathogen is a disease that can have many different effects. These are combined together by a pathologist, so each pathogen you encounter will likely be unique.
A pathogen is defined by several things:
Stats
These are numerical values between 0 and 50 that influence how well the pathogen can do certain things. A pathologist can set these stats directly in the Pathogen Manipulator.
- Advance Rate: This determines how quickly the pathogen will advance through its Stages. (It will also determine how quickly it goes down through the stages under some circumstances.) More on Stages later.
- Spread: This determines how well the pathogen will spread from person to person. This also depends on the pathogens Symptoms. More on Symptoms later. A pathogen with 0 spread will not spread naturally.
- Suppression Threshold: This determines how easily a pathogen can be suppressed via its Suppressant. More on Suppressants later.
A pathogen has only a limited amount of points to spread over these stats, so if it is very good in some stats, the other stats will probably be lower to compensate. The amount of points a pathogen has to spread is known as its Passive Capacity.
Microbody Type
The specific type of pathogen. There are four different types (plus a fifth that only occurs when the admins bombard the station with diseased burgles).
A specific sample has a specific type, and it is unchangeable, so you will need to find a sample with the type you want and then build off of that for your disease.
The microbody type influence a handful of things:
- Stages: The maximum stage that the pathogen can reach. More on stages later.
- Active Capacity: This determines how many symptoms (and of what length) the pathogen can support. Adding any more will destroy the pathogen. More on symptoms later.
- Activity: How often the pathogen can trigger its symptoms. This also differs depending on the pathogens stage.
- Growth Medium: What type of Growth Medium needs to be added to a petri dish in order for the pathogen to grow. This is a chemical.
- Anti-Agent: What type of Anti-Agent needs to be used to make a cure in the Synth-O-Matic. This is a chemical.
- Vaccinable: If a Vaccine can be made for the pathogen.
- Auto-Immunization: If you are immune to the pathogen after you have been cured of it once.
Here are the different microbody types:
| Microbody | Stages | Activity | Active Capacity | Growth medium | Anti-agent | Vaccinable | Self- immunization |
Admin-only |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virus | 5 | 1, 5, 20, 30, 40 | 12 | Egg | Antiviral Agent | Yes | Yes | No |
| Parasite | 5 | 50, 40, 30, 20, 10 | 18 | Parasitic Medium | Biocide | No | No | No |
| Bacterium | 3 | 30, 30, 30 | 25 | Bacterial Medium | Spaceacillin | Yes | Yes | No |
| Fungus | 1 | 10 | ∞ | Fungal Medium | Biocide | Yes | No | No |
| Great Mutatis | 5 | 20, 20, 20, 20, 20 | ∞ | Stable Mutagen | Mutation Inhibitor | No | No | Yes |
For instance, lets say you are infected by a virus. It starts out in stage 1 (as all infections do). While in stage 1, it will only have a 1% chance to trigger it's symptoms, which is very low! But as it progresses through the stages, it will trigger more and more, with up to a 40% chance to possibly trigger symptoms at stage 5.
Something like a Parasite, on the other hand, will start out at 40% in stage 1, so it might spread very quickly! But as it progresses through the stages, it will trigger a bit less (though still a fair amount). This can be helpful for diseases meant to spread quickly, or that have symptoms where it doesn't really matter how much they trigger, because they mainly have passive effects.
A bacterium has a constant activity, so it always triggers at an ok rate, but it can only progress up to stage 3. This means that the symptoms will be a bit weaker, and some really strong effects may never be able to trigger (stuff like gibbing from tier 5 symptoms, for instance). The main advantage of the bacterium though, is that it you can put a lot more symptoms on it than on a virus or parasite, so you might want to go for it if you want a wide variety of effects that are maybe a bit weaker.
Now, you may be thinking, hold on, the fungus is complete garbage! You are correct, the main purpose of a fungus is for it to be used to cultivate lots of symptoms on it, even if you never intend to actually infect anyone with the fungus. You will see what this comes in handy for later, in the section on how to find new symptoms!
Suppressant
The Suppressant, like the microbody type, is an inherent, unchangeable property of a pathogen sample. It is a specific type of stimulus that the pathogen is weak to. When a pathogen is exposed to its suppressant, it might start to regress through its stages, becoming less powerful. Prolonged exposure might even cause it to go into remission, eventually being cured completely. There are a handful of different suppressants, which can be applied in different ways.
You aren't told explicitly what a pathogens suppressant is, it requires a little bit of detective work! Suppressants are split into a few different groups, a quick inspection with a health analyzer or microscope will tell you the group, but not the exact suppressant itself. To find out the precise type, you then simply put a petri dish with a sample of the pathogen under a microscope and use a dropper to drip a little bit of a related chemical into the dish. If the pathogen reacts, you will know that you found the correct suppressant! You can also tell what the suppressant is by the color that the pathogen is when seen under a microscope.
| Group | Suppressant | Trigger | Color | Associated Chemicals |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal | Heat | Afflicted needs to have a high body temperature | Blue | Phlogiston, Chlorine Trifluoride |
| Cold | Afflicted needs to have a low body temperature | Red | Cryostylane, Cryoxadone | |
| Sedative | Sedative | Afflicted needs to sleep | Green | Morphine, Ketamine |
| Muscle Relaxant | Afflicted needs to have related chemicals in bloodstream, or receive electric shocks | White | Haloperidol, Neurotoxin | |
| Medical | Brute Medicine | Afflicted needs to have related chemicals in bloodstream | Black | Styptic Powder, Synthflesh |
| Burn Medicine | Afflicted needs to have related chemicals in bloodstream | Cyan | Silver Sulfadiazine, Synthflesh | |
| Gastronomical | Fat | Afflicted needs to have related chemicals in bloodstream | Orange | Partially Hydrogenated Space-Soybean Oil, Space-Soybean Oil, Porktonium, Cholesterol |
| Chicken Soup | Afflicted needs to have related chemicals in bloodstream | Pink | Chicken Soup | |
| Radioactive | Radiation | Afflicted needs to be irradiated | Viridian | Radium, Unstable Mutagen, Uranium, Polonium |
| Mutagen | Afflicted needs to have related chemicals in bloodstream | Olive Drab | Unstable Mutagen, Stable Mutagen |
Suppressants also have a use in manufacturing cures, but these days they aren't really necessary any more.
Symptoms
Symptoms, aka, the fun part of Pathology!
They are what determines what your Pathogen will actually do! Most of the time in creating a Pathogen goes into finding the Symptoms you want.
Each Symptom has a unique code that is made of segments. Each segment is a combination of three letters or digits. There are five different tiers of Symptoms, with tier 1 Symptoms being the weakest, but only needing one segment, while tier 5 are the strongest, but are made of five segments.
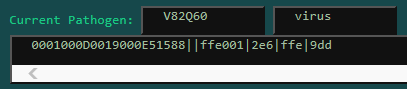
Everything after the || is the Pathogen's Symptoms! The individual Symptom's codes are separated with |, so as you can see, we have four different Symptoms, one tier 2 Symptom (ffe 001) and three tier 1 Symptom (2e6, ffe, 9dd)!
Examining Symptoms
Now, how do we find out which Symptoms these codes correspond to? For this we will use our good friend, the microscope! ![]()
Remove your sample from the Pathogen Manipulator and put it into a petri dish. Then put the petri dish into the microscope, so you can inspect it!
(If you think you might take a while, you may want to put some of the appropriate nutrient type into the petri dish as well, or your sample might starve.)
Clicking the microscope will then allow you to view the sample in two different ways, either zoomed-out or zoomed-in. For checking Symptoms, you'll want the zoomed-in view!
This is going to give you something like this:
The first part of this (suppressed by something affecting neural activity) shows that the Pathogen's Suppressant is of the sedative variety.
The next part is a bunch of hints, the code next to the hint shows you which Symptom code gave them. Now we just need to figure out what Symptoms these hints are referring to. For this we have a helpful reference guide for the different types of Symptoms!
Pathogen Symptoms & Mutations
Now, armed with the knowledge that 'ffe001' is a tier 2 symptom with the hint 'The pathogen appears to generate a high amount of fluids.' we can figure out that it must be either the Sneezing or the Coughing Symptom.
If we wanted to find out which one of the two, we could get ourselves some Pepper from the kitchen and use a Dropper to drip some of it into the petri dish.
After that you can look at the Sample again and you may notice something different:
As we can see in the last part, the Sample exhibits the behavior of Sneezing when it interacts with Pepper, so we know that it is Sneezing, and not Coughing!
If this seems like a lot of work for one Symptom, don't worry, most of the time you can figure out what a Symptom is without needing to test with Chemicals. Also, you don't always need to figure out exactly what all the smaller Symptoms do, if you are going for big ones anyway!
Finding new Symptoms
Ok, now you may be wondering, all these samples I have contain tier 3 Symptoms at best! What if I want my Pathogen to turn everyone into a pile of ash??
That is where finding new Pathogen Symptoms comes in!
For this, we are going to use the DNA Analyzer!
First, we are going to press the 'Split DNA' button, watch out, this will destroy the currently active Sample in the Pathogen Manipulator!
The destroyed Sample's Symptoms will be broken up into the individual Segments and you will be able to combine the Segments to try to find new Symptom Codes.
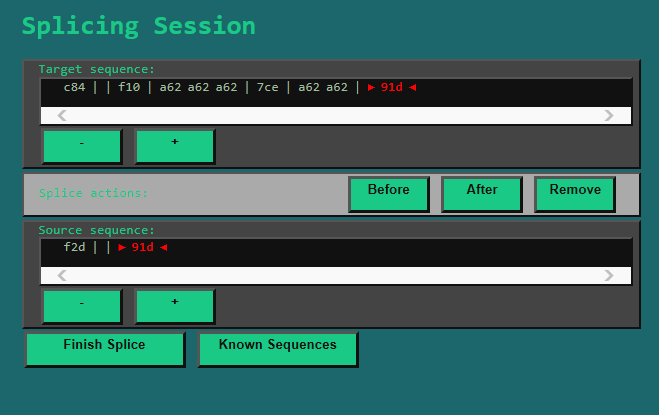
So let's say we split the following Pathogen:
We will receive the following Segments:
(Plus a 'a62' that I accidentally used up before making the screenshot. :))
Of course, you don't need to do this completely at random! Once you have tested a combination, the lights on the right side will show you some information about that attempt!
If your combination was Stable, that means that it is a valid Symptom that you can put into a Pathogen!
If it was Transient that means that while it is not necessarily Stable, there is another Symptom Code that starts with your combination that is Stable.
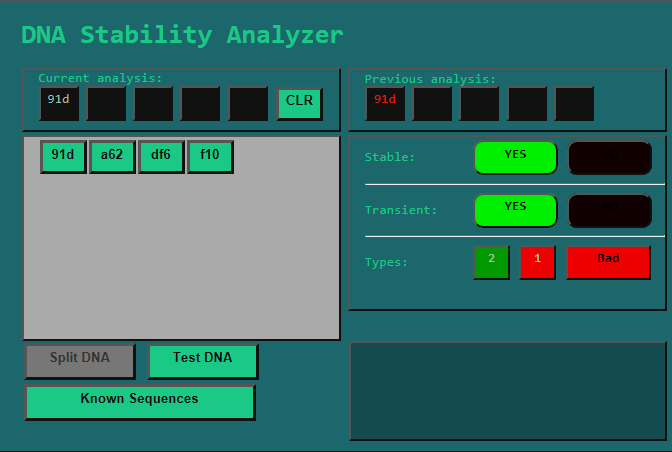
For instance, let's say we test the combination '91d':
We see that '91d' is both Stable and Transient.
This means that we could put '91d' as a Symptom into a Pathogen and it would work! (Which makes sense, since it was already in the Pathogen that we split.)
Furthermore, it also tells us that there is at least one other valid Symptom that starts with '91d'.
Now, if we look a bit lower, we will see that the Types analysis tells us that there are 2 Good Transient Symptoms and 1 Bad Transient Symptom.
Symptoms are split into two categories, Good Symptoms are generally the kind that a person would be happy to have, while Bad Symptoms are usually the ones that harm the Afflicted.
The big red lamp on the right side that says "Bad" tells us what kind the symptoms we just tested is.
So, to sum it up, we now know that:
- '91d' is a valid Symptom. It is of the "Bad" variety.
- There are three other Symptoms that start with '91d', two of them Good, one of them Bad.
So, naturally, our next step would be to try to add more Segments on to '91d', to see if we can find one of those higher tier Symptoms!
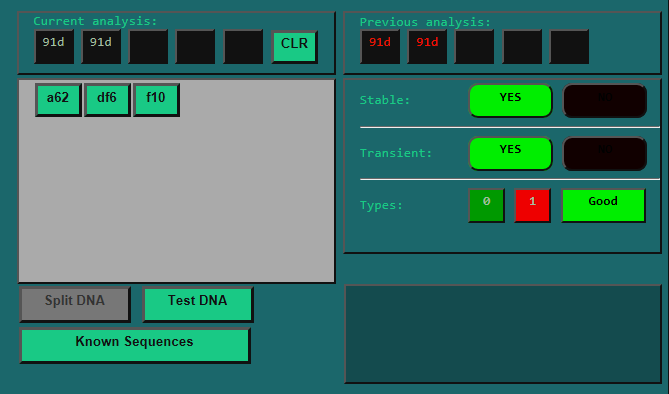
Huzzah! As you can see, this is also a valid Symptom! It is even transient, so there is another Symptom of at least Tier 3 that starts with '91d 91d'.
We also now know that '91d 91d' is a Good Symptom, which might be nice if we are a non-traitor pathologist.
If we check the Pathogen Symptoms & Mutations page, we see that it must be one of the following:
- Detoxication
- Oxygen Farts
- Wound Mending
- Burn Healing
On the other hand, if you are a traitorous pathologist, you may wish to instead try more combinations that start with '91d 91d' in order to find the higher tier symptom that is harmful.
There are always 6 different Segments in each round, but you can see that the pathogen we split only had 4 different Segments. (91d, a62, df6, f10)
This means that I may not necessarily be able to find this higher tier Symptom with the Segments I have available, because what if the combination I need is something like '91d 91d aca'?
For this reason it is usually a good idea to first make a Fungus with every kind of Segment (and lots of them, so you can use them to combine more often before having to load in a new sample).
Splicing Pathogens
Alright, so how do we make a testing pathogen for finding new combinations? And how do we put the combinations we find into an actual pathogen?
Well, for this we will be using the Splicing system!
First of all, we should get ourselves plenty of different samples. This can be done at the Synth-O-Matic! ![]()
For making a testing pathogen, I recommend using a Fungus, since it can support an infinite amount of Segments. Other microbodies will collapse if you try to Splice too many Symptoms onto them! (See Section on Microbodies)
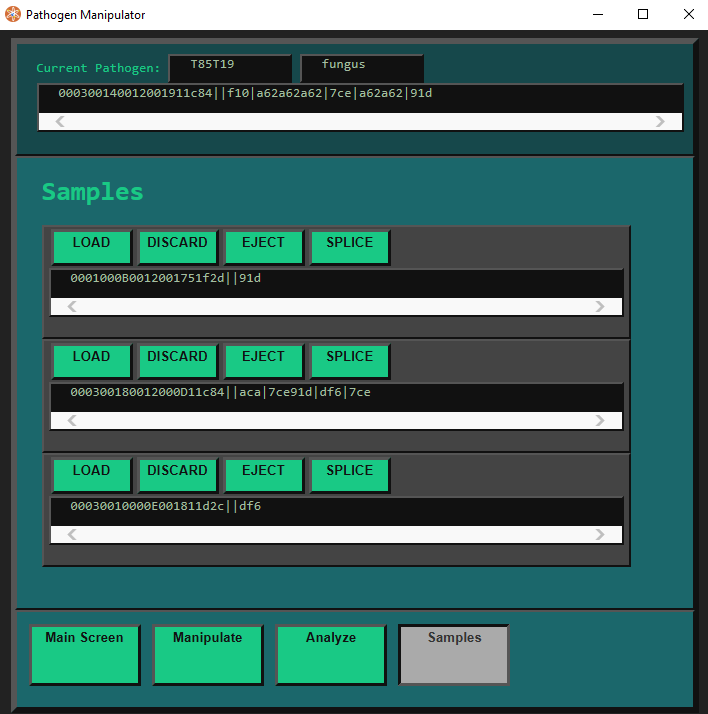
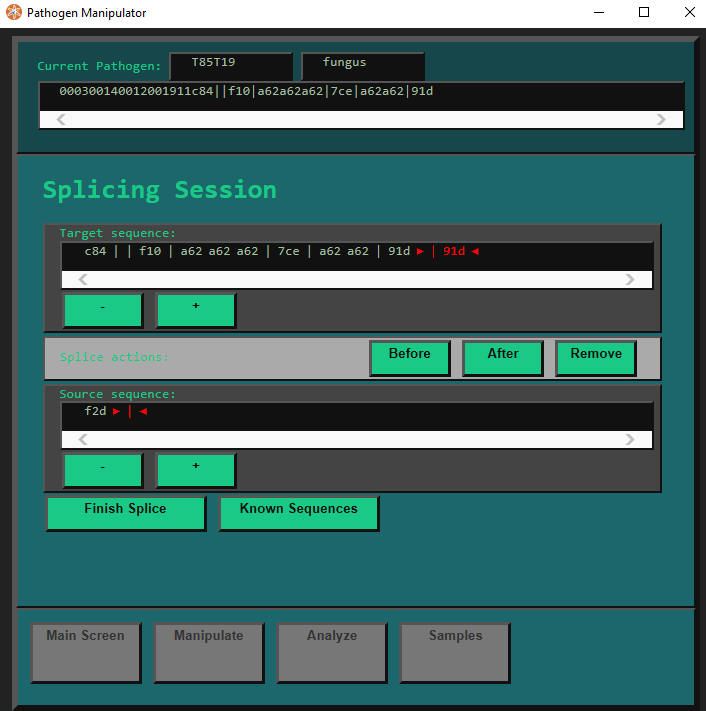
Once you have your Samples, just put them all into the Pathogen Manipulator by clicking. It can hold up to 4 at a time. (Counting the currently active Sample.)
Next, simply click a SPLICE button to start splicing the active Sample together with the Sample whose SPLICE button you clicked.
Now you can splice any Symptom Segments you want from the bottom Sample into the top Sample with the Before and After buttons.
The Remove button can be used to remove any Segments you do not want.
The + and - buttons let you change the size of your selection, so you can transfer more than one Segment at once.
Remember that all the Symptoms (the stuff between the |s) in the top Sample will need to be valid Symptoms, or the Sequence will collapse and the Sample will be lost!
The Sequence will also collapse if the amount of Symptom Segments exceeds the Microbodies' Active Capacity. (as mentioned in the section on Microbodies).
Another tip: the part before the || is the Suppressant code, do not modify it, and do not attempt to put the one from the bottom into the top sample. There is no point and it'll probably mess up your Sample.
(In this case that would be f2d.)
Here is what we end up with in this case:
Once you are done, click the Finish Splice button.
Now we do this for all the other Samples too, and end up with a really long Supersample, which we can use to experiment and find new Symptom Codes!
Growing more Pathogen
Of course, using the DNA Analyzer on a Sample will destroy the Sample, and we wouldn't want to use up the Sample we just put so much work into, right?
That is why we simply make it grow to obtain more Samples that are exactly the same as our initial one!
For this, simply put the sample from the vial into a petri dish. Then add some nutrients to the petri dish, of the appropriate type for the microbody. (See the table up in the microbody section.)
After a minute or two the pathogen will start to grow at a pretty rapid rate, you can just fill it into vials to get more samples.
A sample needs to have at least 2 units of pathogen (a mechanical dropper can be used to transfer exactly 2 units).
All you need to watch out for is the pathogen running out of nutrients and not to remove the last bit of pathogen from the petri dish.
You can also use the Incubator, it will automatically keep one petri dish supplied with nutrients, and you can use a vial on it to fill it with pathogen (if there is enough in the petri dish).
If you are familiar with a reagent heater, the Incubator looks exactly the same. ![]()
Handling Infections
Alright, you've found a bunch of Symptoms, put them on the kind of Microbody you want and adjusted the Stats to your liking! Now what?
Well, infecting someone is very easy! Simply inject the pathogen into their bloodstream and they will be infected with it. This also works with blood extracted from an afflicted person.
Splashing it on them can also work, but it depends on their disease resistance, which is mainly modified by their clothing. Naturally, a biosuit/hood or a spacesuit/helmet combo will protect against any diseases splashed onto a person.
Assuming that your pathogen has one or more spreading Symptoms (coughing, sneezing, farting, hugging, etc...) and a Spread Stat that is not 0, it will also be able to spread itself! How exactly this goes down depends on the Symptom in question, you can read up on this on the Pathogen Symptoms & Mutations page.
One important thing to remember is that some Symptoms make disease clouds. If you are not breathing from and air tank, you will breathe these in, rendering your protective suit useless, so make sure to use internals!
Curing Disease
Oh no, there is a horrible disease going around the station and for some reason it is your duty to cure it! Don't worry, there are several ways you can accomplish this, and most of them are pretty simple.
QM
Do you have Cargo access? Do you really not want to bother with pathology? Then this is the way for you!
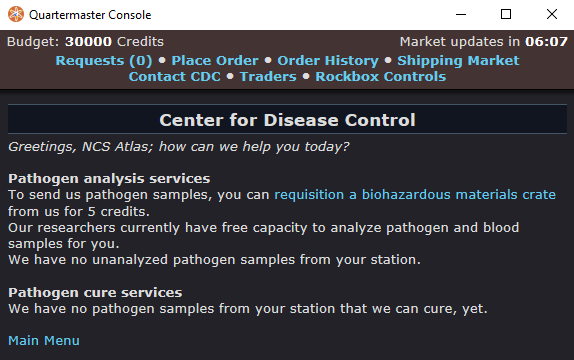
Simply go to the Cargo Console and use the Contact CDC button.
Then requisition a Biohazard Material Crate from them.
Shortly after the crate will arrive, just like any other kind of QM crate.
Now just put a sample of the pathogen into the crate and send it back out, as if you were selling something. The easiest way to do this is to just take blood from an infected person. The CDC even send an empty syringe in the crate for just that purpose!
Shortly after the CDC should be ready to start analysis on the sample you sent, simply click on analyze some samples and then click on the sample you want analyzed. Presumably there will be only one, it's pretty rare that several samples get sent to the CDC in a round!
They analyze the sample pretty much instantly, once that has happened you can simply order batches of cures from them that will then arrive shortly after, just like regular QM orders.
Each batch contains several cures, simply stab an infected person with one of these, and their pathogen will go into remission. It will then slowly go down through the stages and cure itself once it is done.
Cure Manufacturing
Do you like doing things the proper way? Did the traitor pathologist not blow up the lab after they were done? Then this is the correct way for you!
Simply take a blood sample from an infected person using a syringe. Then inject the blood into a blood slide. There are some around the lab and in the path-o-matic vendor.
Next, put the blood slide into a microscope and check what kind of Microbody you are dealing with. You will need to know this to figure out the appropriate anti-agent. (See table in Microbody section.)
Then put the blood slide and a clean petri dish into a centrifuge and start it. ![]()
After a short time, you should have a proper pathogen sample inside the petri dish. Simply give it nutrient to grow more of it as outlined in the Pathogen Growing section earlier.
Put some of the samples from this into vials and put the vials into the Synth-O-Matic. ![]()
Then add some of the appropriate anti-agent from the Path-O-Matic vendor and pick the anti-agent option when putting it in. Don't worry about the suppressant option, it is not necessary right now.
Once both things are in the Synth-O-Matic, simply click the vial in the list of inserted vials and then select the Synthesize serum by irradiation option.
After a second or two, the machine should spit out some cures. If you did everything correctly, these should work to put the infection into remission. (If you did not, they will instead infect people.)
Suppressants
Do you not have access to QM or a Pathology Lab? Do you not want to do any fancy science stuff? Then this is the section for you.
Figure out the Suppressant as described in the section on Suppressants up above. Then expose yourself to it until your Pathogen goes into remission. It's that simple!
A humble health analyzer will tell you the Suppressant Group of the disease. From then you really only have two different options that you need to try. You'll know you have the right Suppressant if you get a message about feeling better, or if the Stage of your Infection (as seen on the health analyzer) decreases.